Scrumb
What is Scrumb ?
SCRUMB is a complex product development framework. Its creators define it as an iterative holistic framework. It is a method that relies on dividing a project into “time boxes”, referred to as “speed peaks”.
To begin with, learn more about Scrumb on :
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Scrum_(software_development)
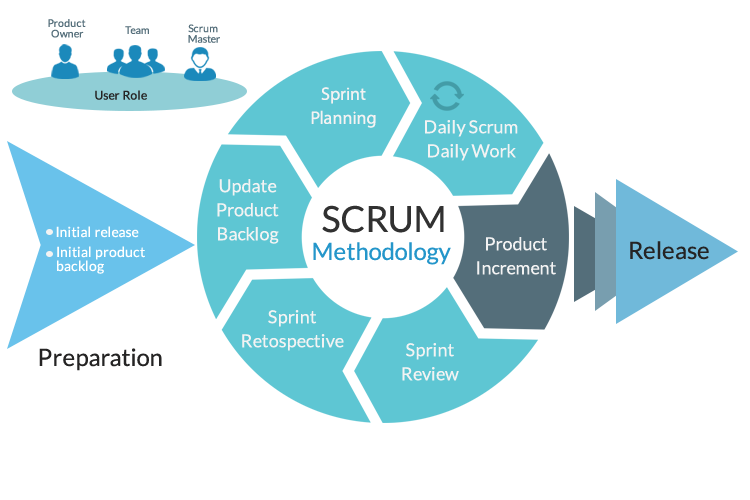
What is srumb ?
These sprints may last longer or shorter, but at the beginning, some operational planning is put in place in order to know the spread over time.
Each sprint finishes with a final demonstration, before starting one again. You get a retrospective to find out what worked, what didn’t, and learn from mistakes in order to be more effective. Every manager is at the same level, there is no hierarchy. SCRUMB is widely used in different fields such as software, aeronautics or building.
Scrum is an empirical process based on three pillars: transparency, inspection and adaptation. It also follows the principles of agile culture.
Scrum focuses on having a common language between all the actors involved in the product. This common language should enable any observer to quickly gain a good understanding of the project and its progress. At regular intervals, Scrum offers to take stock of the various artifacts produced, in order to detect any undesirable variations. If a drift is detected during the inspection, then the process must be adapted. Scrum provides “events”, during which this adaptation is possible. These are the sprint planning meeting, the daily melee, the sprint review and the sprint retrospective.
Scrum is based on the conviction that software development is inherently non-deterministic and that all the activities involved in implementing a complex project cannot be anticipated and planned.
This is why Scrum opposes predictive approaches such as the V-cycle or CMMI. To respond to this unpredictability, the Scrum method offers a process control model based on empiricism, through continuous adaptation to real business conditions and rapid response to changes
The analysis of the actual operating conditions during the end-of-sprint retrospectives and the resulting continuous improvement plan are carried out at regular intervals, giving rise to an incremental development cycle (Sprint).
Scrum was designed during software development projects. It can also be used by maintenance teams. In the case of very large projects, teams multiply and we speak of large-scale scrum (e.g. the scrum de scrums or LESS).
Except for the maintenance of product and iteration logs, there are no process elements described in the reference documentation that require the use of a particular tool. In Agile Project Management with Scrum, Ken Schwaber gives the example of product and iteration logs maintained in a spreadsheet, which also allows the calculation of burndown charts (“progress charts”) 12. Burndown charts are only mentioned in the Scrum Guide as an example and are not a required practice.
Here a visualisation of Scrumb process :
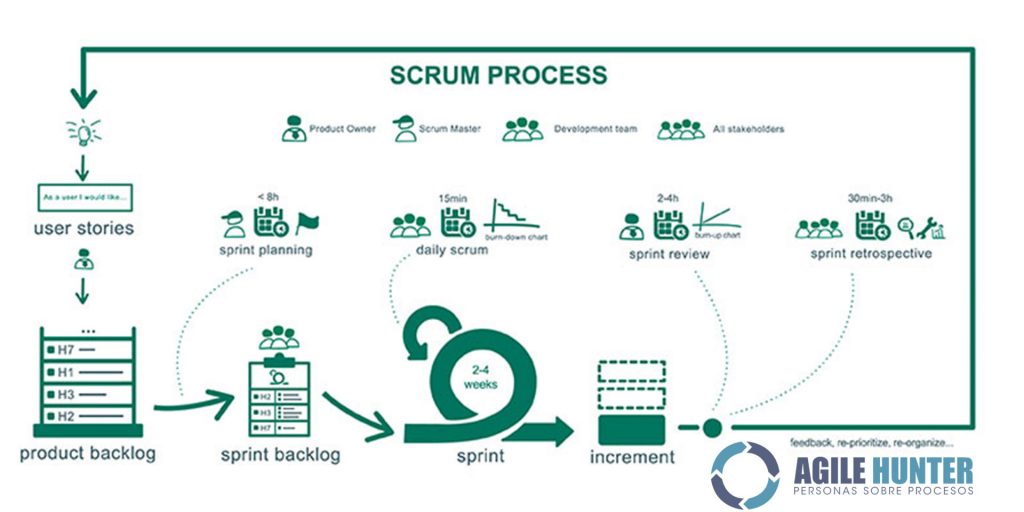
Learn more about Scrumb process :
